Author: Austin Lim
Orders of Magnitude
| Number | Power of 10 | Name | Prefix
(symbol) |
Example in biology (approx) |
| 0.000000000000000001 | 10-18 | Quintillionth | atto- (a) | |
| 0.000000000000001 | 10-15 | Quadrillionth | femto- (f) | |
| 0.000000000001 | 10-12 | Trillionth | pico- (p) | |
| 0.000000001 | 10-9 | Billionth | nano- (n) | 20 nanometers = synapse length |
| 0.000001 | 10-6 | Millionth | micro- (µ) | 10 micrometers = neuron diameter |
| 0.001 | 10-3 | Thousandth | milli- (m) | 2 milliseconds = duration of action potential |
| 1 | 100 | 1.7 meters = height of a human | ||
| 1,000 | 103 | Thousand | kilo- (k) | 20 kilohertz = highest pitch humans can hear |
| 1,000,000 | 106 | Million | mega- (M) | |
| 1,000,000,000 | 109 | Billion | giga- (G) | 86 billion = neurons in the brain |
| 1,000,000,000,000 | 1012 | Trillion | tera- (T) | 150 trillion = synapses in the brain |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000 | 1015 | Quadrillion | peta- (P) | |
| 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 | 1018 | Quintillion | exa- (E) |
Units of Measurement
| Measurement | Unit (short) | Examples |
| Length | Meters (m) | Length of wavelength of visible light: 500 nanometers Length of a typical neuron: 20 micrometers
Height of a typical human: 1.7 meters |
| Volume | Liters (L) | Volume of cytoplasm in a single spin: 0.1 femtoliters Volume of CSF in ventricles: 150 milliliters |
| Weight | Grams (g) | Weight of typical brain: 1.3 kilograms
Weight of typical grown adult human: 70 kilograms |
| Time | Second (s) | Duration of action potential: 2 millisecond |
| Velocity | Meters per second (m/s) | Speed of slow action potential propagation: 0.1 m/s Speed of fast action potential propagation: 100 m/s |
| Concentration | Molar (M) | Calcium ion concentration in cell: 100 nanomolar Sodium ion concentration in ACSF: 140 millimolar |
| Temperature | Celsius (C) Kelvin (K) | Freezing point of water: 0 Celsius or 273 Kelvin Typical body temperature: 37 Celsius or 310 Kelvin |
| Electrical potential | Volts (V) | Charge of a typical neuron: -70 millivolts |
| Current | Ampere (A) | Current passing through single ion channel: 5 picoamps |
| Resistance | Ohm (Ω) | Typical input resistance of neuron: 200 megaohms |
| Conductance | Siemens (S) | Conductance through single ion channel: 10 picosiemens |
| Capacitance | Farad (F) | Capacitance in neuron: 100 picofarads |
| Magnetic field | Tesla (T) | Strength of fMRI machine: 5 Tesla |
| Frequency | Hertz (Hz) | Range of human hearing: 20 Hertz to 20 kilohertz |
| Loudness | Decibels (dB) | Pain threshold: 130 dB Conversation: 65 dB |
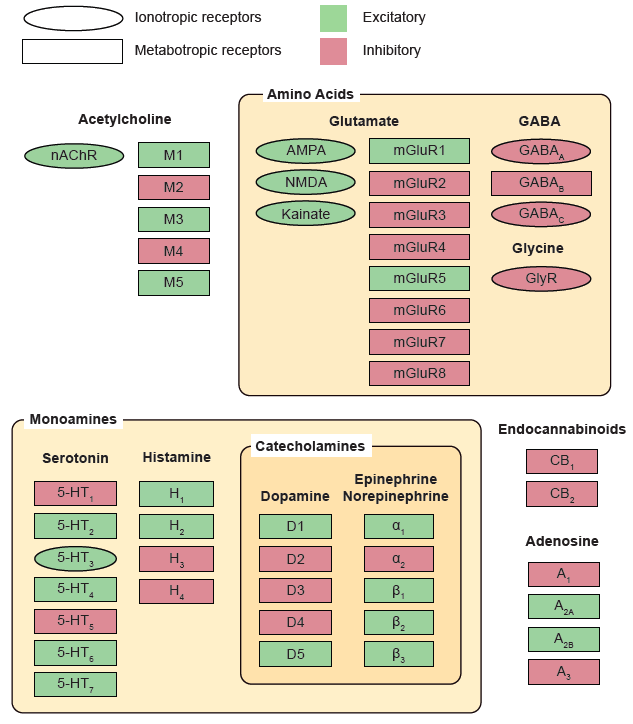
Neurotransmitters and their Receptors
Brodmann Areas and Functions
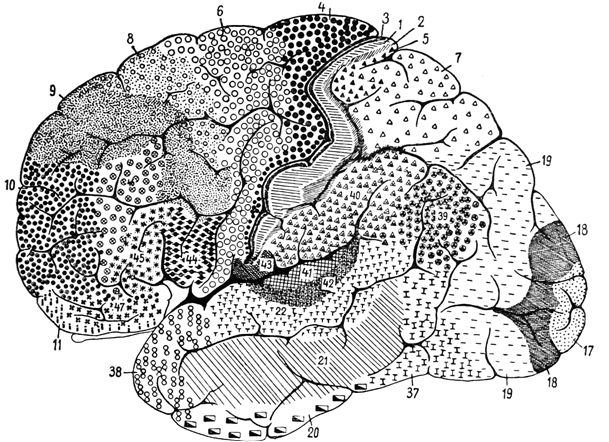
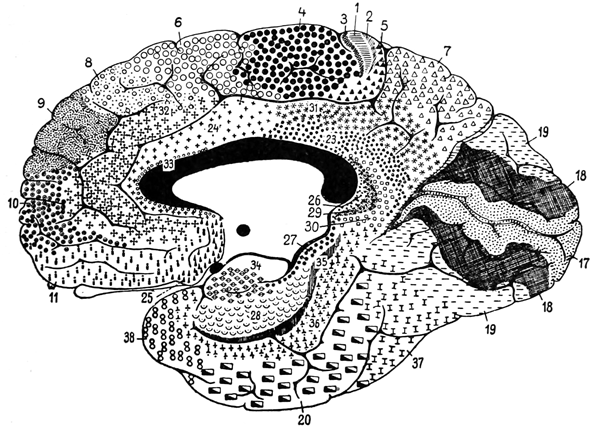
| Brodmann area | Name | Function |
| 1, 2, 3 | Primary somatosensory cortex (S1) | Touch sensory and perception |
| 4 | Primary motor cortex (M1) | Voluntary motor control |
| 5 | Superior parietal lobule | Identification of objects based on somato-sensory cues (stereognosis) |
| 6 | Premotor; supplemental motor | Limb movement planning |
| 7 | Posterior parietal association area | Integration of visual and motor |
| 8 | Frontal eye fields | Visual perception and motor, saccades |
| 9, 46 | Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex | High order executive functions |
| 10 | Anterior prefrontal cortex | High order executive functions |
| 11, 12 | Orbitofrontal area | Emotion, decision making |
| 13, 14, 16 | Insular cortex | Emotion, empathy, taste, homeostasis |
| 15 | Anterior temporal lobe | Social knowledge and memories |
| 17 | Primary visual cortex (V1) | Vision, pattern recognition |
| 18 | Secondary visual cortex (V2) | Vision, illusory contours |
| 19 | Associative visual cortices | Vision, color, motion, depth |
| 20 | Inferior temporal gyrus | Visual memory, face perception |
| 21 | Middle temporal gyrus | Visual memory, emotional recognition |
| 22 | Superior temporal gyrus | Language comprehension, attention, hearing |
| 23, 31 | Posterior cingulate cortex | Emotions |
| 24, 32, 33 | Anterior cingulate cortex | Emotions, attention, decision making |
| 25 | Subgenual area | Inhibition of emotion, decision making |
| 26 | Ectosplenial area | Emotions |
| 27 | Presubiculum | Emotions, head direction |
| 28, 34 | Entorhinal cortex | Memory, navigation, smell, emotions |
| 29, 30 | Retrosplenial cortex | Memory, navigation |
| 35, 36 | Perirhinal cortex | Perception, memory |
| 37 | Fusiform gyrus | Facial processing, perception |
| 38 | Temporopolar area | Socio-emotional processing, smell |
| 39 | Angular gyrus | Reading, speech, perception |
| 40 | Supramarginal gyrus | Language perception and processing |
| 41, 42 | Auditory cortex (A1) | Hearing |
| 43 | Gustatory cortex | Taste |
| 44, 45, 47 | Broca’s area | Language, movement planning, cognition |
| 48 | Retrosubicular area | Memory |
| 49 | Parasubicular area | Navigation |
| 52 | Parainsular area |
Location of Brodmann Areas
Lateral View
Midsagittal View
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cholinergic_synapse.svg
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Human_Brodmann_areas_(K._Brodmann,_1909,_p._131,_Fig._85-86).jpg

